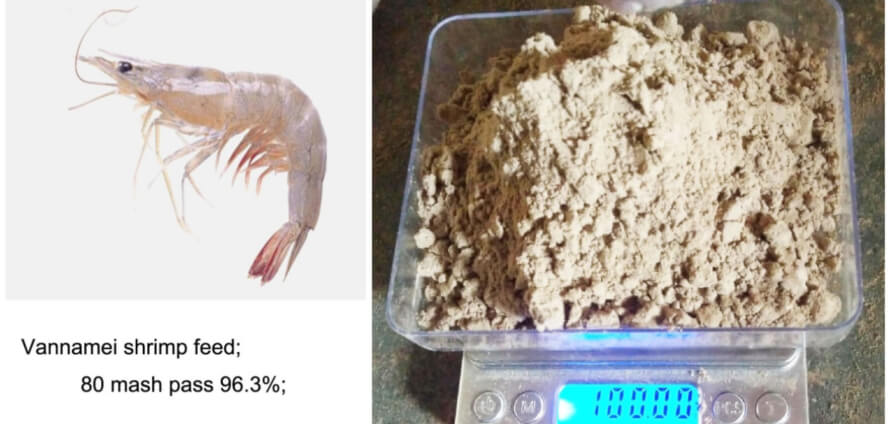
Feeds for prawns and other aquatic animals must be finely crushed to meet the needs of animal digestion and granulation. The fineness of material grinding may be affected by factors such as animal growth stages, nutritional needs, and feed processing technology and equipment. Therefore, a reasonable choice of grinding fineness is also an inevitable requirement for reducing costs, increasing production capacity and ensuring product quality.
1.Aquatic Animal Nutrition Requirements for Grinding Fineness
From a nutritional point of view, the smaller the crushed particles of the material, the more surface area there is to contact with digestive enzymes, so as to achieve a higher digestion utilization rate. Studies have shown that excessively fine grinding in suckling pig feed may lead to peptic ulcers, but no such studies have been reported in aquatic animals.
Generally speaking, the digestive tract of aquatic animals is short. In order to speed up digestion and absorption, the crushing particle size of aquatic feed should be smaller than that of livestock and poultry feed. For example, the particle size of eel and prawn feed should reach 80-120 mesh. In addition, the compound feed for aquatic animals has high protein content, low carbohydrate content, and the feed particle structure is compact, requiring high cohesiveness and water resistance. The nutritional requirements of these aquatic animals have put forward requirements for the reasonable crushing of feed.

2.Production and processing requirements for grinding fineness and particle size distribution
Proper grinding fineness plays an important role in processing. The smaller the crushing fineness of the material, the easier it is to absorb the steam in the conditioner, so that the gelatinization is more complete. In addition, finer materials require relatively less extrusion force during granulation or extruding. If the crushing fineness is too large, the energy consumption will increase relatively when passing through the ring die and pressing rollers, and it will affect the quality of granulation and puffing, resulting in the feed particles being easily broken and the stability in water is also poor. There is a similar situation in extrusion granulation. When the material particles are large, it often takes more energy to crush the large particles. In addition, some granulators cannot crush large material particles due to the problem of extrusion structure, which may easily cause blockage of the ring die, thus affecting the output and product quality.
In addition to the fineness of crushing, the distribution range of the particle size of the material also has a very important influence on the processing. In general, the smaller the particle size distribution range of the material, the better. For example, in the process of puffing, a large difference in crushing particle size will lead to a lower level of starch gelatinization in the conditioner, because in this case more energy is required to gelatinize larger material particles. For the production process of pulverizing first and then batching, since the raw materials are pulverized separately in the pre-processing stage, it is difficult to limit the particle size to a relatively narrow range in the subsequent mixing section. Therefore, the general aquatic feed production process adopts the first batching and then crushing process or the secondary crushing process, which can make the particle size range of the material relatively uniform. In addition, reasonable screening of materials after secondary crushing is also an effective measure to improve the uniformity of crushing.

3.Requirements of Feed Mixing Uniformity on Grinding Fineness
For aquatic animals, pellet feed must meet a certain degree of stability in water in order to meet the feeding needs of animals. In order to obtain high water stability of the feed, on the one hand, the fineness of the material is required to be fine enough, on the other hand, it is also required that the feed raw materials can be mixed evenly. From the perspective of uniform mixing, it is generally required that 95% of the material can pass through the 177-250μm sieve. Especially for the production of particles with a diameter of 0.8-1.5 mm or smaller, the requirements for crushing fineness are even higher. When determining the fineness of feed crushing, there is a basic principle that the diameter of the largest particle of crushing should not be greater than 1/3 of the ring die. This principle is related to the size of the ring die, which determines the crushing particle size of the feed.
4.Requirements of Feed Floating and Stability on Grinding Fineness
The feed of prawns and other aquatic animals not only requires the satisfaction of nutrition, but also their feeding habits determine whether to adopt the production design of sinking or floating feed. Generally speaking, a good crushing particle size makes the feed easy to form a tight bond, thereby increasing the density of the pellets and making the feed easier to sink. In addition, the smaller pulverized particles have larger surface area, which makes the particles more tightly combined during pelleting, thereby preventing the feed from soaking and collapsing, and improving the stability of the feed in water. If the particles are not tightly combined, the feed will easily collapse in the water and affect the water quality.
5.Reasonable choice of grinding equipment
Different types of pulverizers and changes in the structure of the pulverizer have a considerable impact on the pulverized materials. At present, the pulverizers commonly used in the production of aquatic feed mainly include hammer mills and ultrafine pulverizers. Generally, the ultrafine pulverizer is suitable for pulverizing the feed with high protein, high fat and low cellulose content. On the contrary, the feed with high fiber, low protein and low fat is suitable for pulverizing with a hammer mill. For different crushing equipment, air assist is very important. Pneumatically conveying the crushed material serves two important purposes. It conveys the shredded product from the shredder to the receiving unit and cools the contents of the shredding chamber with ambient air. The ultrafine pulverizer is mainly used in the production of extruded feed or pellet feed smaller than 2.5mm. The ultrafine pulverizer does not have a screen like a hammer mill, nor does it have a high-speed rotating hammer. The pulverizer is usually completed by a superfine pulverizer, pneumatic conveying, and a classifier. It uses the strong power of the air flow to drive the materials, and the materials collide with each other under the drive of the gears to reduce the size of the particles, so that they are distributed to various parts of the pulverizer chamber. The speed of the impact gear can reach 31,000rpm, so it can produce very fine particles. However, compared with the traditional pulverizer, the energy consumption of the superfine pulverizer is relatively large, and finer pulverized materials are also prone to problems such as electrostatic adsorption.
Like a pulverizer, a hammer mill also uses airflow to squeeze material. The material is thrown to the hard wall of the inner chamber by the hard hammer for impact so that the particles are broken, and the material bounces back from the inner chamber and is hit again by the rotating hammer. The material finally contacts the sieve at a small angle with the internal velocity of the hammer, and the diameter decreases again. At present, the commonly used water drop hammer mill changes the crushing chamber from a circular shape to a water drop shape, which not only increases the effective screening area of the sieve plate in the crushing chamber, but also destroys the material to form a circulation in the crushing chamber, which is beneficial to the crushed material. After being discharged from the crushing chamber, the crushing efficiency is greatly improved, and the average particle size of the crushed material is 100-500 μm. The crushing effect of hammer mill varies with the level of fat, fiber and protein in the material, but generally speaking, hammer mill is most suitable for crushing fiber feed. When the feed fat is high, the crushing effect will decrease due to the clogging of the screen.
Generally, when producing ordinary fish feed, the particle size of raw materials is required to be 40-60 mesh, but when producing special aquatic pellet feed (shrimp feed, eel feed, etc.), the particle size of raw materials must be above 80 mesh. Therefore, when choosing crushing equipment for aquatic feed enterprises, many factors must be considered at the same time, such as production varieties, crushing fineness requirements, quality, price, work efficiency and production cost of crushing equipment.
At present, feed manufacturers mainly focus on the following aspects when choosing a pulverizer: ① How to make the pulverized material reach the required particle size and reduce the energy loss during the pulverization process. At present, many equipment manufacturers adopt measures such as increasing the screening area, destroying the circulation layer of the grinding chamber, increasing the opening of the sieve plate, and strengthening the air suction after grinding to improve the grinding efficiency.
② The durability of the vulnerable parts of the pulverizer is also an important factor to consider when choosing a pulverizer. High-quality hammers can reduce the consumption of hammers in the pulverization process and increase the output of the pulverizer per unit time.
③ The optimization of the machining accuracy and assembly accuracy of the pulverizer is also an important consideration when selecting the pulverizer.





